Upward Social Mobility
Discover insights about upward social mobility and their relevance in today's dynamic business environment.
This change may involve improvements or setbacks in wealth, education, and health, among others. Households are evaluated by the Espinosa Yglesias Studies Center (CEEY) according to the following categories:
Households without Educational Lag516
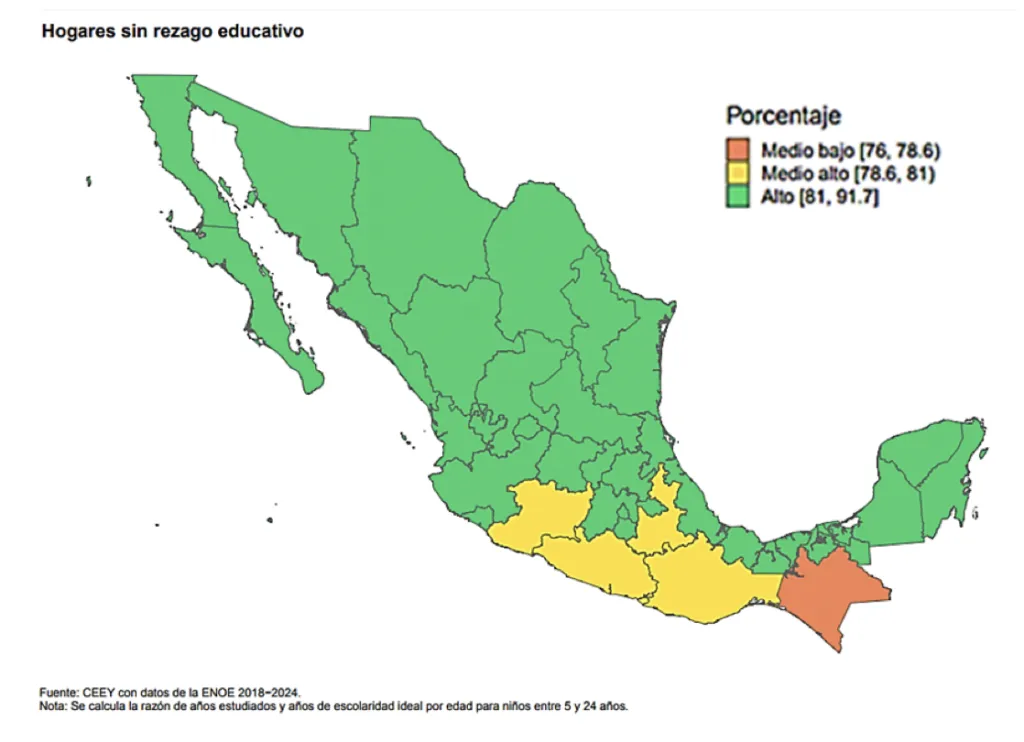
It is the proportion of years studied among the ideal years of schooling for the population group between 5 and 24 years of age.
The percentage of the population between 5 and 24 attending classes should be greater than 81%, which has been achieved in most states, but not all with quality education.
Households with Social Security866
It is the percentage of households in which at least one of its members has access to a social security institution.
Social security should be universal, but within the current conditions in Mexico, we have populations in which only half or a third of households have access to it.
Persistence in the First Quintile (lowest Income)1194
It is the percentage of households that remained in the group with the lowest income (quintile I) for one year.
When a year passes and the households detected in the first quintile or those with the lowest income remain without favorable changes, it is taken for granted that social mobility in that entity is zero and that the households in question could continue in that situation permanently.
Households without Employed Persons with Remuneration1655
It is the percentage of households where no member reports receiving a salary.
4
26% of Mexico’s GDP is made up of unpaid work, usually carried out by housewives when cleaning, cooking, caring for and supporting the multiple activities of the home, and to which more and more other family members are added because many of them have to work.
Due to the lack of a National Care System, many households have members who, although they work, do not report receiving a salary for their activities, and they can represent up to a third of households per state.
Social Mobility
All households whose children are starting from the twenty-fifth step are evaluated, predicting, based on the variables that allow upward movement, what step they will reach in their adulthood.
Thus, in Chiapas, according to current conditions, a child positioned on step 25 could rather go down to 21 instead of accessing 26 or higher. This is not the case in Nuevo León where the same child could well have the conditions to climb to level 46, that is, practically to a double scale of his current position.
In the regional neighborhood we have mobilities from 35 to 42, with Aguascalientes presenting the level 40 step.
The 2030 Agenda states that all people should have access to basic goods, societies as a whole must seek maximum social mobility, through: eradicating poverty through inclusive economic growth, the creation of sustainable jobs and the promotion of equality.
More Articles

Why the León Fair is Key to Guanajuato's Economy
Jan 12, 2026

ART WKND GDL 2026 to Boost Jalisco's Economy: Which Galleries to Visit?
Jan 27, 2026

2026 World Cup: Guadalajara's Investment Strategy, FIFA Criteria, and Urban Benefits
Jan 8, 2026

How is Nuevo León Preparing to Welcome Millions of Border Crossings?
Jan 8, 2026

Dollar at 17 Pesos: Challenge or Relief for Nuevo León's Economy?
Jan 27, 2026

LatAm Urges Regional Unity Amidst Venezuela Conflict
Jan 5, 2026
